C#.NET 实体框架EF(Entity Framework)详解

目录
一、什么是Entity Framework
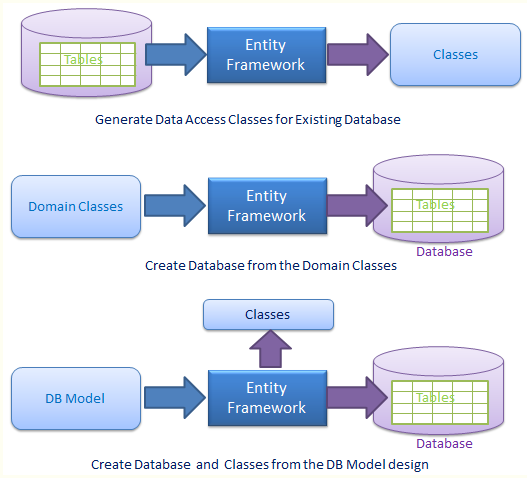
微软官方提供的ORM工具,ORM让开发人员节省数据库访问的代码时间,将更多的时间放到业务逻辑层代码上。EF提供变更跟踪、唯一性约束、惰性加载、查询事物等。开发人员使用Linq语言,对数据库操作如同操作Object对象一样省事。EF有三种使用场景,
- 从数据库生成Class
- 由实体类生成数据库表结构
- 通过数据库可视化设计器设计数据库,同时生成实体类。
ORM是什么?
ORM 是将数据存储从域对象自动映射到关系型数据库的工具。ORM主要包括3个部分:域对象、关系数据库对象、映射关系。
ORM使类提供自动化CRUD,使开发人员从数据库API和SQL中解放出来。
二、Entity Framework 架构
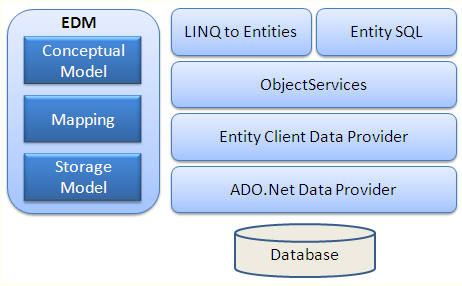
EDM (实体数据模型):EDM包括三个模型,概念模型、 映射和存储模型。
概念模型 ︰ 概念模型包含模型类和它们之间的关系。独立于数据库表的设计。
存储模型 ︰ 存储模型是数据库设计模型,包括表、 视图、 存储的过程和他们的关系和键。
映射 ︰ 映射包含有关如何将概念模型映射到存储模型的信息。
LINQ to Entities ︰ LINQ to Entities 是一种用于编写针对对象模型的查询的查询语言。它返回在概念模型中定义的实体。
Entity SQL: Entity SQL 是另一种炉类似于L2E的言语,但相给L2E要复杂的多,所以开发人员不得不单独学习它。
Object Services(对象服务):是数据库的访问入口,负责数据具体化,从客户端实体数据到数据库记录以及从数据库记录和实体数据的转换。
Entity Client Data Provider:主要职责是将L2E或Entity Sql转换成数据库可以识别的Sql查询语句,它使用Ado.net通信向数据库发送数据可获取数据。
ADO.Net Data Provider:使用标准的Ado.net与数据库通信
三、Entity Framework运行环境
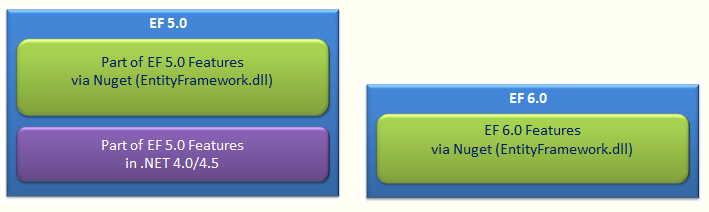
EF5由两部分组成,EF api和.net framework 4.0/4.5,而EF6是独立的EntityFramework.dll,不依赖.net Framework。使用NuGet即可安装EF。
四、创建实体数据模型
使用向导创建实体类,或键添加,傻瓜式的~
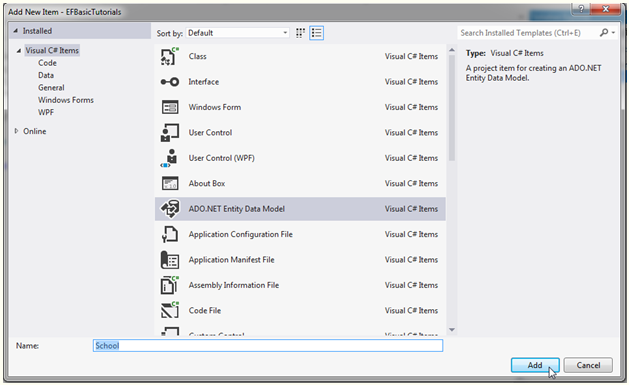
添加完成之后,.config文件中会添加以下配置
<?xmlversion="1.0"?>
<configuration>
<configSections>
<!-- For more information on Entity Framework configuration, visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=237468 -->
<sectionname="entityFramework" type="System.Data.Entity.Internal.ConfigFile.EntityFrameworkSection, EntityFramework, Version=6.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089"requirePermission="false"/>
</configSections>
<startup>
<supportedRuntimeversion="v4.0"sku=".NETFramework,Version=v4.5"/>
</startup>
<entityFramework><defaultConnectionFactorytype="System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.SqlConnectionFactory, EntityFramework"/>
<providers><providerinvariantName="System.Data.SqlClient"type="System.Data.Entity.SqlServer.SqlProviderServices, EntityFramework.SqlServer"/>
</providers>
</entityFramework>
<connectionStrings><addname="SchoolDBEntities"connectionString="metadata=res://*/SchoolDB.csdl|res://*/SchoolDB.ssdl|res://*/SchoolDB.msl;provider=System.Data.SqlClient;provider connection string="data source=.\sqlexpress;initial catalog=SchoolDB;integrated security=True;multipleactiveresultsets=True;application name=EntityFramework""providerName="System.Data.EntityClient"/>
</connectionStrings>
</configuration>
Context & Entity 类:
每个Entity Data Model 生成一个context类,类数据库每个表生成一个entity类。如在School.edmx中包含的两个重要的文件{EDM Name}.context.tt和{EDM Name}.tt:
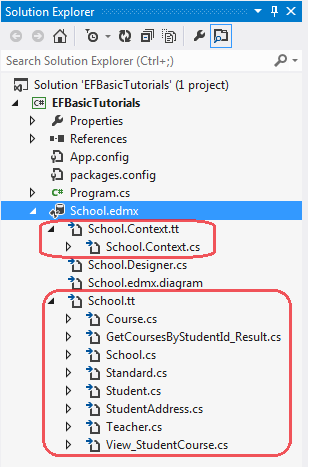
School.Context.tt:T4模板用于生成的context类,可以从目录结构中看到School.Context.tt下包含一个School.Context.cs文件。
School.tt:用于生成表映射的实体类。Entity类是POCO类。如Student生成
public partial class Student
{
public Student()
{
this.Courses = new HashSet<Course>();
}
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; }
public Nullable<int> StandardId { get; set; }
public byte[] RowVersion { get; set; }
public virtual Standard Standard { get; set; }
public virtual Student Address StudentAddress { get; set; }
public virtualI Collection<Course> Courses { get; set; }
}
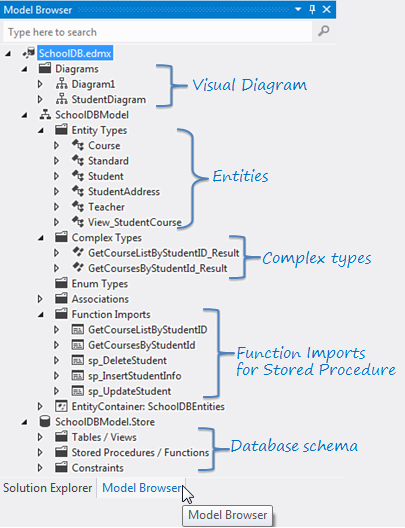
五、模板浏览器
以SchoolDB为例,切换到Model View视图下,看到类图结构:
六、DBContext
第四节中提到EDM生成SchoolDBEntities类,该类从System.Data.Entity.DbContext类继承。EntityFramework4.1中Context类从ObjectContext类继承。DbContext类与ObjectContext类似,它对ObjcetContext类进行包装更利于开发的三种模式:CodeFirst、Model First、Database First.
DbContext是EntityFramework很重要的部分,连接域模型与数据库的桥梁,是与数据库通信的主要类。
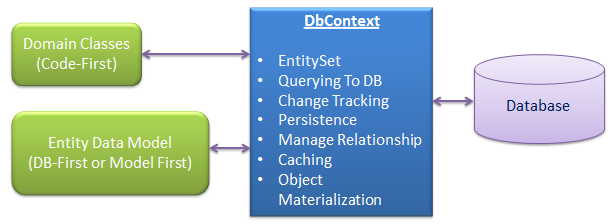
DbContext主要负责以下活动:
EntitySet:DbContext包含了所有映射到表的entities
Querying:将Linq-To-Entities转译为Sql并发送到数据库
Change Tracking:从数据库获取entities后保留并跟踪实体数据变化
Persisting Data:根据entity状态执行Insert、update、delete命令
Caching:DbContext的默认第一级缓存,在上下文中的生命周期中存储entity
Manage Relationship:DbContext在DbFirst模式中使用CSDL、MSL、SSDL管理对象关系,Code first中使用fluent api 管理关系
Object Materialization:DbContext将物理表转成entity实例对象
DEMO
DbContext实例化:
using (var ctx = newSchoolDBEntities())
{
//Can perform CRUD operation using ctx here..
}
将DbContext转为ObjectContext
using (var ctx = newSchoolDBEntities())
{
var objectContext = (ctx as System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.IObjectContextAdapter).ObjectContext;
//use objectContext here..
}
七、Entity Framework中的Entity类型
POCO Entity (Plain Old CLR Object):
不依赖于任何Framework的类的类(also known as persistence-ignorant objects),为Entity Data Model生成CRUD命令服务。
public class Student
{
public Student()
{
this.Courses = new List<Course>();
}
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; }
public Nullable<int> StandardId { get; set; }
public Standard Standard { get; set; }
public StudentAddress StudentAddress { get; set; }
public IList<Course> Courses { get; set; }
}
Dynamic Proxy (POCO Proxy):
Dynamic Proxy是运行时POCO类的代理类,类似POCO类的包装。Dynamic Proxy允许延迟加载(Lazy loading),自动跟踪更改。POCO Entity必需满足以下几点才能转为POCO Proxy:
1. 必需声明为public 类
2. 不可以是sealed类
3. 不可以是抽象类
4. 导航属性必需是public,vitual(Entity包含两种属性,标量属性Scalar properties:Entity本身的字段值,Navigation properties:其它entity的引用如班级-学生)
5. 集合属性必需是 ICollection<T>
6. ProxyCreationEnabled 选项必需是true
public class Student
{
public Student()
{
this.Courses = new HashSet<Course>();
}
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; }
public Nullable<int> StandardId { get; set; }
public virtual Standard Standard { get; set; }
public virtual StudentAddress StudentAddress { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Course> Courses { get; set; }
}
八、Entity Relationships:
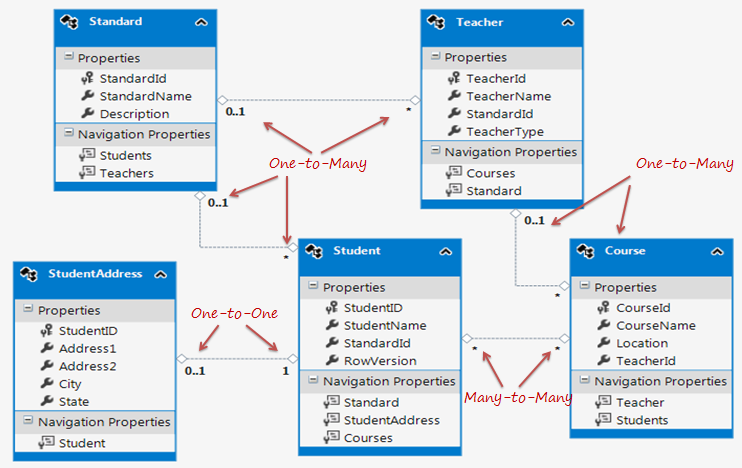
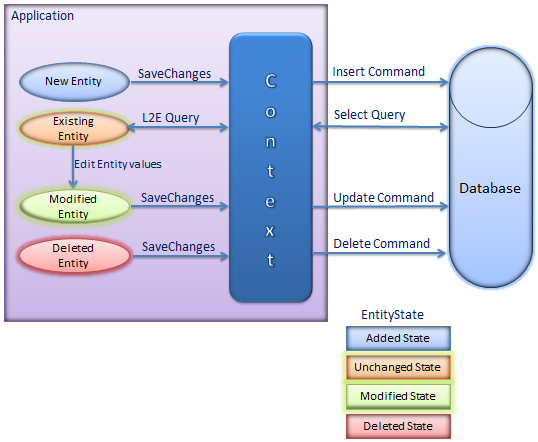
九、 Entity Lifecycle
在我们做CRUD操作时,要先了解EntityFramework如何管理实体状态。每个实体的生命周期内都会在DbContext上下文中保存一个状态,分别是Added Deleted Modified Unchanged Detached
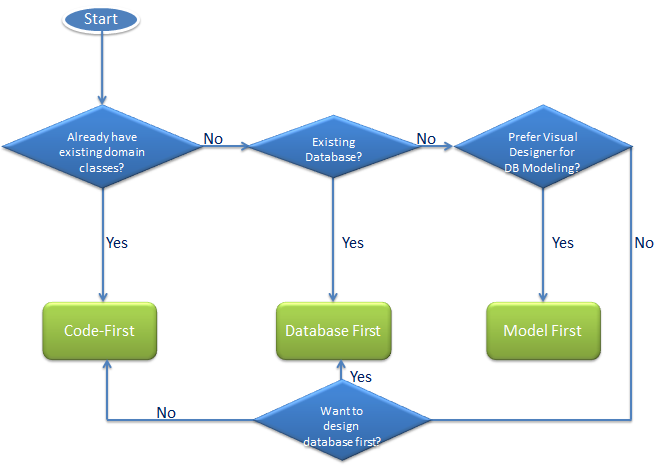
十、Code First、DBFirst、Model First
CodeFirst 领域设计时先定义实体类,用实体类生成数据库
DbFirst 从数据库生成实体类
Model First 使用Visual Studio实体设计器,设计ER,同时生成Entity类和DB
十一、使用查询
三种查询方式
1) LINQ to Entities,
2) Entity SQL,
3) Native SQL
LINQ to Entities:
LINQ Method syntax:
//Querying with LINQ to Entities
using (var context = newSchoolDBEntities())
{
var L2EQuery = context.Students.where(s => s.StudentName == "Bill");
var student = L2EQuery.FirstOrDefault<Student>();
}
LINQ Query syntax:
using (var context = new SchoolDBEntities())
{
var L2EQuery = from st in context.Students
where st.StudentName == "Bill"select st;
var student = L2EQuery.FirstOrDefault<Student>();
}
Entity SQL:
//Querying with Object Services and Entity SQL
string sqlString = "SELECT VALUE st FROM SchoolDBEntities.Students " +
"AS st WHERE st.StudentName == 'Bill'";
var objctx = (ctx as IObjectContextAdapter).ObjectContext;
ObjectQuery<Student> student = objctx.CreateQuery<Student>(sqlString);
Student newStudent = student.First<Student>();
//使用EntityDataReader
using (var con = newEntityConnection("name=SchoolDBEntities"))
{
con.Open();
EntityCommand cmd = con.CreateCommand();
cmd.CommandText = "SELECT VALUE st FROM SchoolDBEntities.Students as st where st.StudentName='Bill'";
Dictionary<int, string> dict = newDictionary<int, string>();
using (EntityDataReader rdr = cmd.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.SequentialAccess | CommandBehavior.CloseConnection))
{
while (rdr.Read())
{
int a = rdr.GetInt32(0);
var b = rdr.GetString(1);
dict.Add(a, b);
}
}
}
Native SQL:
using (var ctx = newSchoolDBEntities())
{
var studentName = ctx.Students.SqlQuery("Select studentid, studentname, standardId from Student where studentname='Bill'").FirstOrDefault<Student>();
}
十二、跟踪变更与持久化场景
在连接状态下持久化与脱机状态下持久化
连机状态下持久化,在同一个DbContext中不需要销毁Entity,直接写入数据库
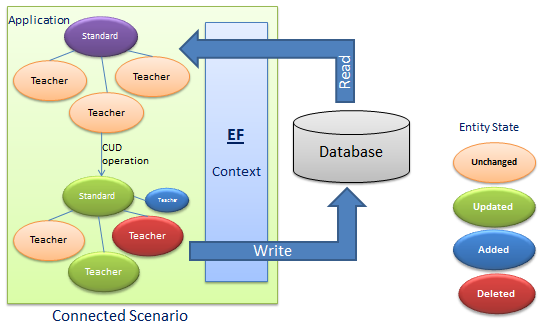
脱机状态持久化指读取和保存Entity在两个不同的DbContext中,Context2不知道Entity的更新状态,所以必需通知Context2当前的Entity做了何种更新。
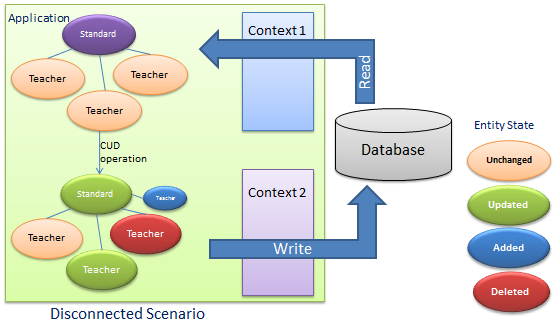
Context只在DbSet上跟踪添加和删除
正确的添加和删除
using (var context = new SchoolDBEntities())
{
var studentList = context.Students.ToList<Student>();
//Perform create operation
context.Students.Add(newStudent() { StudentName = "New Student" });
//Perform Update operationStudent studentToUpdate = studentList.Where(s => s.StudentName == "student1").FirstOrDefault<Student>();
studentToUpdate.StudentName = "Edited student1";
//Perform delete operation
context.Students.Remove(studentList.ElementAt<Student>(0));
//Execute Inser, Update & Delete queries in the database
context.SaveChanges();
}
以下代码在List中添加和删除不起作用,只有更生有效
using (var context = new SchoolDBEntities())
{
var studentList = context.Students.ToList<Student>();
//Add student in list
studentList.Add(new Student() { StudentName = "New Student" });
//Perform update operationStudent studentToUpdate = studentList.Where(s => s.StudentName == "Student1").FirstOrDefault<Student>();
studentToUpdate.StudentName = "Edited student1";
//Delete student from listif (studentList.Count > 0)
studentList.Remove(studentList.ElementAt<Student>(0));
//SaveChanges will only do update operation not add and delete
context.SaveChanges();
}
脱机实体
脱机实体管理要先附加到Context
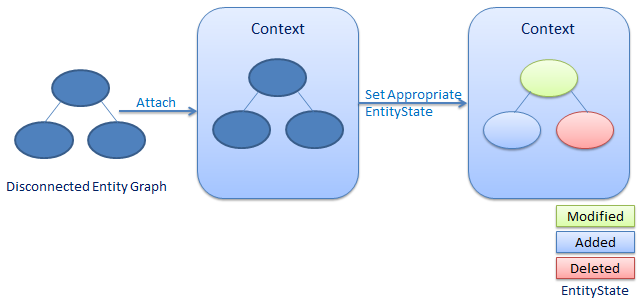
//disconnected entity
graphStudent disconnectedStudent = newStudent() { StudentName = "New Student" };
disconnectedStudent.StudentAddress = newStudentAddress() { Address1 = "Address", City = "City1" };
using (var ctx = newSchoolDBEntities())
{
//attach disconnected Student entity graph to new context instance - ctx
ctx.Students.Attach(disconnectedStudent);
// get DbEntityEntry instance to check the EntityState of specified entity
var studentEntry = ctx.Entry(disconnectedStudent);
var addressEntry = ctx.Entry(disconnectedStudent.StudentAddress);
Console.WriteLine("Student EntityState: {0}",studentEntry.State);
Console.WriteLine("StudentAddress EntityState: {0}",addressEntry.State);
}添加多个关系实体时与添加单个实体一样,更新关系实体时需要跟踪每个实体的状态。
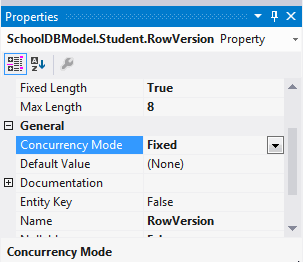
十三、Entity Framework并发处理
添加RowVersion,类型为TimeStamp字段,在EDM中X修改并发属性为Fixed。EF更新实体时会先检查RowVersion,如果发现RowVersion不一致,则抛出DbUpdateConcurrencyException异常
十四、贪婪加载、惰性加载与定向加载
贪婪加载:使用Include(),自动加载关联实体
using (var context = new SchoolDBEntities())
{
var res = (from s in context.Students.Include("Standard")
where s.StudentName == "Student1"
select s).FirstOrDefault<Student>();
}
执行Sql
SELECTTOP (1)
[Extent1].[StudentID] AS [StudentID],
[Extent1].[StudentName] AS [StudentName],
[Extent2].[StandardId] AS [StandardId],
[Extent2].[StandardName] AS [StandardName],
[Extent2].[Description] AS [Description]
FROM [dbo].[Student] AS [Extent1]
LEFTOUTERJOIN [dbo].[Standard] AS [Extent2] ON [Extent1].[StandardId] = [Extent2].[StandardId]
WHERE'Student1' = [Extent1].[StudentName]惰性加载:延迟加载对象关联的实体,用到时再加载,EF默认为LazyLoading
using (var ctx = newSchoolDBEntities())
{
//Loading students onlyIList<Student> studList = ctx.Students.ToList<Student>();
Student std = studList[0];
//Loads Student address for particular Student only (seperate SQL query)
StudentAddress add = std.StudentAddress;
}
定向加载:Reference()和Collection() 方法
using (var context = new SchoolDBEntities())
{
//Loading students only
IList<Student> studList = context.Students.ToList<Student>();
Student std = studList.Where(s => s.StudentID == 1).FirstOrDefault<Student>();
//Loads Standard for particular Student only (seperate SQL query)
context.Entry(std).Reference(s => s.Standard).Load();
//Loads Courses for particular Student only (seperate SQL query)
context.Entry(std).Collection(s => s.Courses).Load();
}
十五:执行SQL
返回实体
using (var ctx = newSchoolDBEntities())
{
//列名必需要Entity属性匹配
var studentList = ctx.Students.SqlQuery("Select * from Student").ToList<Student>();
}
返回非实体类型
using (var ctx = newSchoolDBEntities())
{
//Get student name of string type
string studentName = ctx.Database.SqlQuery<string>("Select studentname from Student where studentid=1").FirstOrDefault<string>();
}执行SQL命令
using (var ctx = new SchoolDBEntities())
{
//Update command
int noOfRowUpdated = ctx.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand("Update student set studentname ='changed student by command' where studentid=1");
//Insert command
int noOfRowInserted = ctx.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand("insert into student(studentname) values('New Student')");
//Delete command
int noOfRowDeleted = ctx.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand("delete from student where studentid=1");
}
DbFramework组件框架是基于CSFramework.DB核心库衍生出来的一个实体模型框架,用于提交实体模型数据,支持Add,Delete,Update,Select 对象。
DbFramework组件框架类似EntityFramework,是CSFramework独立自主研发的一个Mini组件。
http://www.cscode.net/archive/CSFRAMEWORK.DB/1631384565.html